Manhattan plots are for GWAS. Archipelago plots are for complex variant association studies.
Archipelago connects variant set association tests and single-variant tests (e.g. GWAS) into a single, interpretable genomic view, without changing how either analysis is performed.
Archipelago is an interpretation layer. Visual standards for large-scale association studies must be reusable across projects, institutions, and publications.
Read moreArchipelago does not perform association testing.
It does not replace GWAS, RVAT, or VSAT methods. It visualises results you already trust.
Variant set association tests are powerful but lack intrinsic genomic coordinates. Single-variant GWAS provides spatial context but misses aggregated effects. Archipelago assigns each variant set a meaningful genomic position derived from its constituent variants, enabling joint interpretation of set-level and variant-level signals in a familiar genome-wide frame.
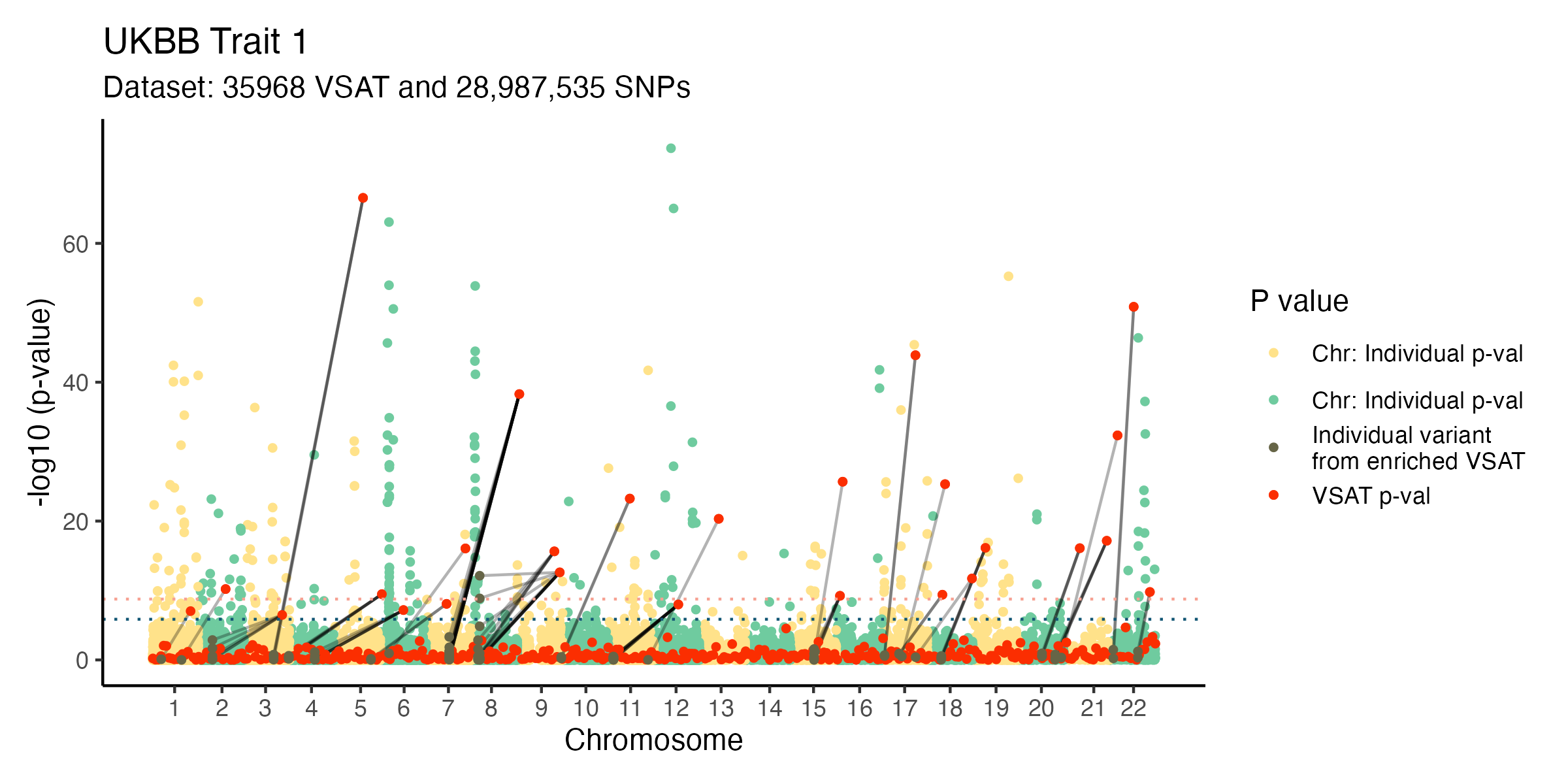
Archipelago plots in BioBank-scale analysis. Pan-UK Biobank (n=469,382) platelet distribution width trait using WES GWAS and DeepRVAT gene-level VSAT (data trimmed at 1e-75 for distracting outliers) (Clarke et al. 2024; Karczewski et al. 2024). GWAS background downsampled. For more examples see the citation below.
When Archipelago is most useful
Archipelago is useful whenever variant collapse is used and an association signal is present.
It applies equally to small cohorts and large population studies. As with any GWAS or RVAT, usefulness depends on detectability, not on sample size alone. Variant collapse increases power within genes, pathways, or other sets; Archipelago then maps those set-level signals back to their underlying genomic drivers.
Archipelago is therefore most informative when set-level and single-variant results need to be interpreted together in genomic context, rather than read as disconnected rankings.
This holds for focused disease cohorts as well as biobank-scale sequencing studies.
Validated use cases
Archipelago has been validated across three complementary settings:
1000 Genomes (1KG)
Small cohort validation demonstrating conceptual correctness and controlled behaviour in pathway-level VSAT combined with GWAS.
Pan-UK Biobank with DeepRVAT
Hundreds of thousands of individuals, millions of SNPs, and gene-level rare variant association tests integrated with GWAS, demonstrating scalability and interpretability.
UK Biobank WGS UTR PheWAS
Whole-genome sequencing with rare non-coding burden, showing how set-level UTR signals map back to individual GWAS variants in a clinically interpretable positive control.
These settings demonstrate Archipelago’s ability to unify association signals across variant resolution and genetic architecture.
Installation
Install the released R package from CRAN:
install.packages("archipelago")
library(archipelago)
Source: cran.r-project archipelago (for installation see below).
Example workflow
Provide two inputs:
- Variant set association test results.
- Single-variant association results annotated with a shared set identifier.
Generate an integrated plot:
archipelago_plot(vsat_results, variant_results)
Archipelago returns a publication-ready figure suitable for dense genome-wide studies.
Demo
install.packages("archipelago")
library(archipelago)
??archipelago()
# example data
data("vsat_pval", package = "archipelago")
data("variant_pval", package = "archipelago")
head(vsat_pval)
# e.g. SKAT-O results
# set_ID P
# 1 1 0.002039443
# 2 2 0.003459603
# 3 3 0.060544051
head(variant_pval)
# e.g. GWAS results
# set_ID BP P CHR SNP
# 1 1 351696 0.9211610 6 351696
# 2 2 988282 0.8652950 9 988282
# 3 3 929171 0.6916336 12 929171
p_basic <- archipelago_plot(
df1 = vsat_pval,
df2 = variant_pval,
output_path = tempfile(),
output_raw = tempfile()
)
print(p_basic)
Citation
If you use Archipelago, please cite the published article.
Manuscript
Lawless, Dylan, et al. “Archipelago method for variant set association test statistics” Genetic Epidemiology (2026).
Preprint |
DOI |
PDF |
Repository |
Application (this page).
@article{2025lawlessArchipelagoMethodVariant,
author = {Lawless, Dylan and Saadat, Ali and Oumelloul, Mariam Ait and Schlapbach, Luregn J. and Fellay, Jacques},
title = {Archipelago Method for Variant Set Association Test Statistics},
journal = {Genetic Epidemiology},
volume = {50},
number = {1},
pages = {e70025},
year = {2026},
doi = {10.1002/gepi.70025},
url = {https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/gepi.70025}
}
Licence
Archipelago is released under the MIT Licence. It may be used, modified, and embedded in research and commercial pipelines without restriction.


